Low-code vs. no-code strategy: how to choose the right approach?
No-code and low code solutions democratise the IT development world and are definitely worth exploring. Let's look at both of them to check when to use them and what are the main differences between them.
Key takeaways on low-code vs. no-code strategy:
- Low-code and no-code development platforms enable users with varying technical skills to create applications quickly and efficiently, democratising software development and empowering business users to build solutions tailored to their specific needs.
- While low-code platforms still require some coding knowledge and offer more customisation options, no-code solutions are designed for non-technical users, providing a visual, drag-and-drop interface to build applications with minimal or no coding required.
- Low-code and no-code approaches can significantly accelerate application development, reduce costs, and enable faster time-to-market, making them attractive options for organisations looking to drive digital transformation and innovation.
What is low-code and no-code?
To put it simply, low-code and no-code development platforms allow users to create applications with minimal or no manual coding, using visual interfaces and pre-built components to streamline the development process.
Both of those solutions are great alternatives for the traditional software development methods which require highly skilled developers to create products. With low-code and no-code solutions software development world opens up and is within easy reach.
Low-code development platforms offer drag and drop interfaces, pre-build templates and reusable components that accelerate the application development process, allowing users to customise components and workflows using configuration rather than traditional programming.
No-code platforms take the concept of low-code development a step further – they allow users to create applications entirely without writing any code.
How is low-code different from no-code development?
The main difference between a low-code and no-code platform is the level of coding involvement required from their users.
While low-code development platforms require some degree of manual coding and developers may still need to write custom scripts or configure certain aspects of the application’s logic, no-code development platforms enable users to create applications entirely without writing any code.
They offer highly intuitive visual interfaces, pre-built templates and modules, allowing users with little or no programming experience to design and deploy functional applications.
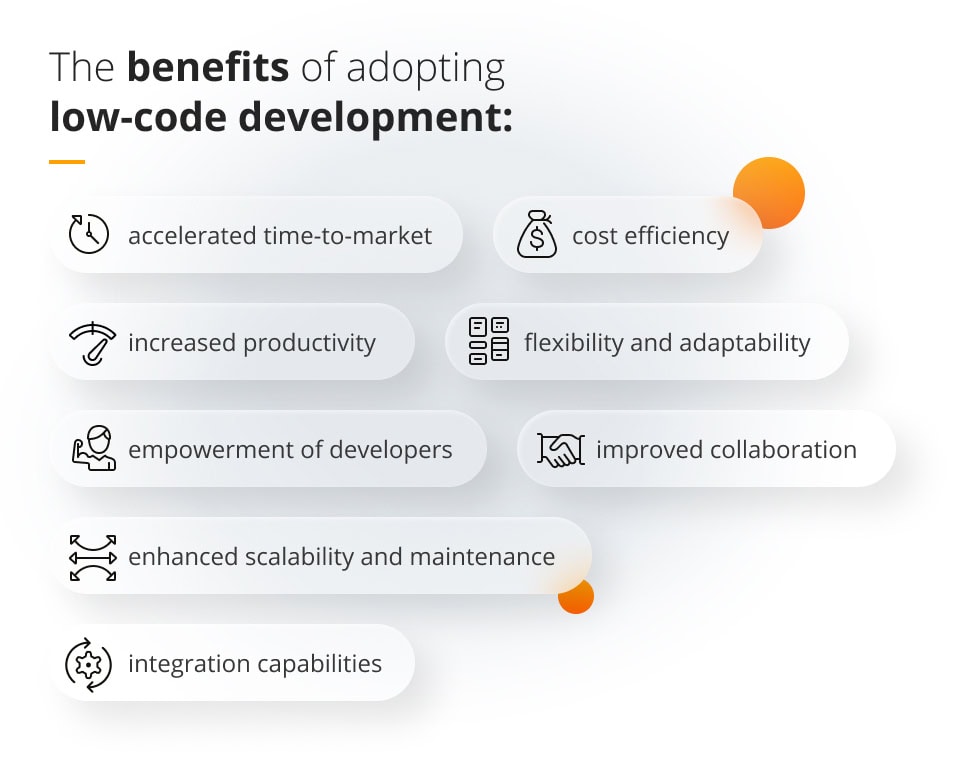
Benefits of using low-code and no-code tools
With their great easiness of use, low-code and no-code tools offer several important benefits, including:
- speed of development: both low-code and no-code platforms accelerate the application development process, allowing to save a lot of time in comparison to traditional coding methods;
- reduced technical complexity: low-code and no-code platforms abstract away much of the technical complexity associated with software development, making it accessible to users with various levels of technical expertise;
- cost effectiveness: by reducing the need for skilled developers and shortening development cycles, low-code and no-code tools can lower overall development costs;
- flexibility and agility: low-code and no-code platforms enable rapid prototyping and iteration, allowing developers to quickly adapt to changing business requirements or market conditions;
- democratisation of technology: both low-code and no-code platforms reduce dependency of highly skilled, expensive and difficult to find IT specialists, allowing businesses to take full advantage of the development world.

Comparative analysis: core features and use cases of low-code and no-code
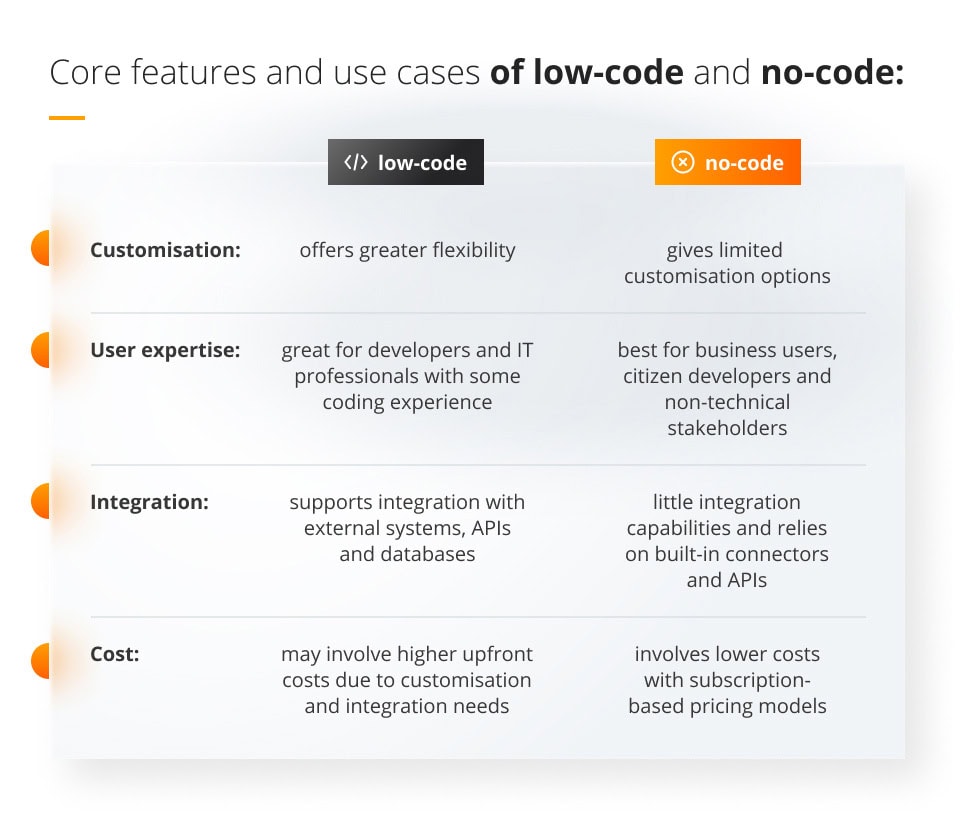
Apart from the level of coding involvement, no-code and low-code tools differ also in other core features. Let’s look at them in more detail:
- Customisation: low-code offers greater flexibility, while no-code gives limited customisation options as it relies on pre-build modules;
- User expertise: low-code development is great for developers and IT professionals with some coding experience, while no-code is best for business users, citizen developers and non-technical stakeholders;
- Integration: low-code supports integration with external systems, APIs and databases, while no-code has little integration capabilities and relies on built-in connectors and APIs;
- Cost: low-code may involve higher upfront costs due to customisation and integration needs, while no-code app development involves lower costs with subscription-based pricing models.
When it comes to their use cases, low-code development platforms are suitable for enterprise-grade applications, integrations, and workflow automation.
No-code approach is best for rapid prototyping, process automation, and business process management.
Contact us
Accelerate your Digital Transformation with low-code/no-code solutions!
When to choose low-code vs. no-code vs. full-code?
Choosing between low-code, no-code, and full-code development approaches depends on several factors, including project requirements, team expertise, time constraints, and budget considerations. Here’s a quick overview which may help you make the right decision:
Low-Code Development:
Choose low-code development when you need to accelerate development cycles, streamline application delivery, and reduce time-to-market.
Think of it also when you have a team of developers with varying levels of coding expertise who can leverage visual tools and pre-built components to build complex applications efficiently.
Such an approach is best for projects that require integration with existing systems, customisation of workflows, and flexibility in application design.
No-Code Development:
No-code development is a great option when you need to empower business users, citizen developers, or non-technical stakeholders to build applications without relying on IT support.
Opt for no-code for projects that involve rapid prototyping, process automation, and simple to moderately complex applications with standardised workflows.
Think of no-code when time-to-market is critical, and you need to quickly iterate on ideas, automate tasks, or solve specific business problems without writing any code.
Full-Code Development:
Full-code development may be for you when you require complete control over the application architecture, logic, and functionality and when you have highly customised requirements, complex business logic, or integration needs that cannot be met by low-code or no-code platforms.
Use full-code when building mission-critical applications, specialised solutions, or projects that demand performance optimisation, scalability, and extensive customisation.
See other articles that may be of interest to you:
- Green Coding: sustainable programming for the planet
- Cutting-edge technology in software development: tech-fueled transformation
- Cloud-based software development: benefits and solutions your business needs
Should your organisation adopt low-code or no-code solutions?
Whether your organisation should adopt low-code or no-code solutions depends on various factors. If you are in the phase of making such a decision, do consider:
- Your business objectives, goals and priorities. If you aim to accelerate digital transformation, improve operational efficiency, and empower business users to innovate, both low-code and no-code solutions can be beneficial.
- Your IT team’s skills and capacity. If you have a team of developers with varying levels of coding expertise, a low-code solution might be suitable as it allows them to leverage their coding skills while accelerating development. If your organisation lacks technical resources or wants to reduce reliance on IT, a no-code solution may be more appropriate.
- Your project’s complexity and scope. Low-code platforms are well-suited for building complex applications, integrating with existing systems, and customising workflows. No-code platforms are ideal for rapid prototyping, automating simple to moderately complex processes, and empowering non-technical users to build applications independently.
- Your time constraints. Both low-code and no-code solutions can expedite development cycles and reduce time-to-market compared to traditional coding methods. Choose the solution that aligns with your timeline and enables you to iterate quickly on ideas.
- Your budget and cost considerations. While low-code and no-code platforms can lower development costs by reducing the need for custom coding and technical resources, they may involve upfront investments in platform licensing, training, and support. Before making a decision, assess the total cost of ownership and ROI of each solution.
- Your long-term growth and scalability requirements. Low-code platforms offer more flexibility and customisation options, making them suitable for scaling complex applications and integrating with diverse systems. No-code platforms are easier to use but may have limitations in terms of scalability and customisation.
When making up your mind do remember that it may also prove beneficial to pilot both types of solutions on small-scale projects and evaluate their effectiveness before scaling up adoption across the organisation!
Low-code and no-code development with Future Processing
Keen to go ahead with some development projects? At Future Processing, we know that a no-code or a low-code development platform may be an answer to many common pain points you may identify in the process of undergoing digital transformation.
Our highly experienced specialists will help you choose the right strategy for your business and will provide you with technical consultancy, guiding you throughout the whole process or assisting you to improve your existing solutions. Get in touch with us today – we will be happy to help!





